The Normal Ear
The human ear can be divided into three sections. Each section performs a different role in transmitting sound waves to the brain.
- Outer ear
- Middle ear
- Inner ear
View the diagrams below to learn more about the different sections of the ear and how we hear.
Parts of the Outer Ear
The outer ear consists of the visible portion on the side of the head, known as the
pinna [1], and the
external auditory canal (ear canal) [2]. The purpose of the pinna is to catch sound waves, amplify them slightly, and funnel them down the ear canal to the
tympanic membrane (eardrum) [3]. The tympanic membrane is a very thin structure that separates the outer ear canal from the middle ear space.
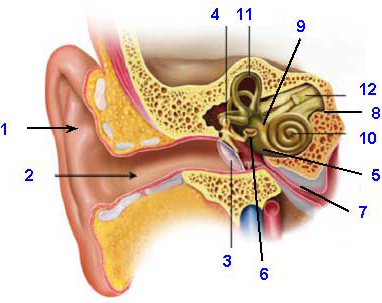
Parts of the Middle Ear
The middle ear is an air-filled cavity that sits between the
tympanic membrane [3] and the inner ear. The middle ear also consists of three tiny bones called ossicles [4], the
round window [5], the
oval window [6], and the
Eustachian tube [7].
Ossicles and Their Function
- Malleus (commonly known as the hammer)
- Incus (commonly known as the anvil)
- Stapes (commonly known as the footplate, or stirrup)
One end of the malleus is attached to the tympanic membrane and the other end is attached to the incus. The incus is attached to the
stapes. The base of the stapes is located in a depression called the
oval window [6]. The oval window membrane is one of two membranes that separate the middle ear space from the inner ear. The other is the round window membrane.
The
Eustachian tube [7] connects the middle ear space to the upper part of the throat. In its normal state, the Eustachian tube stays closed, but it will open when you yawn, swallow, chew, or hold your nose and blow. The purpose of the Eustachian tube is to provide fresh air to the middle ear space and to equalize pressure between the outer ear and the middle ear. Ever wonder why your ears “pop” when you go up or down in an airplane or an elevator in a tall building? That sound is your Eustachian tube(s) opening and closing to equalize the air pressure in your ears.

Parts of the Inner Ear
The inner ear is encased in the
temporal bone [8] and consists of three parts:
-
Vestibule [9]: the central inner ear cavity
-
Cochlea [10]: the organ of hearing
-
Semicircular Canals [11]: part of the balance system
Parts of the Cochlea
The cochlea is made up of three compartments (scala tympani, scala media, scala vestibuli) that are separated from each other by two membranes (basilar membrane and Reissner’s membrane). A tiny organ (organ of Corti) sits on top of the basilar membrane. This organ contains hair cells, which convert the mechanical energy from the vibrations of the basilar membrane into electrical impulses. Those electrical impulses are sent to the
auditory nerve [12], which transmits the information up the brainstem to the auditory cortex.
How We Hear
The pinna catches sound waves and channels them down the external auditory canal, where they hit the tympanic membrane and make it vibrate. Those vibrations cause the three ossicles to move. The stapes footplate pushes on the oval window membrane, which sets the cochlear fluid in motion. This wave-like motion causes the basilar membrane to vibrate. As the basilar membrane moves up and down, the tiny “hairs” (stereocilia) on top of the hair cells open and close to change the electrical charge of the cell. This results in a release of chemicals (neurotransmitter), which signals auditory nerve fibers to fire. The auditory nerve sends these impulses up to the brain, where the signal is interpreted as sound.
-
How Do You Hear? Follow Sound Waves From the Outer to the Inner Ear and Auditory Nerve
Sounds are all around us. We hear when these sounds pass through the outer, middle, and inner parts of our ears - sending thousands of tiny vibrations up to our brain for interpretation. First sound travels through the outer ear canal and makes the eardrum move. When the eardrum moves, the three middle ear bones vibrate. This vibration creates movement of fluid in the inner ear also known as the cochlea. The fluid movement causes sensory receptors in the coiled-shaped cochlea to send a signal along the auditory nerve to the brain, and this is how we hear.
Hearing and Balance
